The video and slides from Simon’s keynote are now online under Courses > One-off events.
Sampling and quantisation
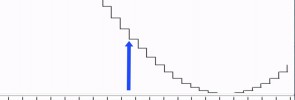
Is digital better than analogue? Here we discover that there are limitations when storing waveforms digitally. We learn that the consequence of sampling at a fixed rate is an upper limit on the frequencies that can be represented, called the Nyquist frequency. In addition to the limitations of sampling, storing each sample of the waveform as a […]
Continue reading...TD-PSOLA …the hard way

Time-Domain Pitch Synchronous Overlap and Add (TD-PSOLA) can modify the fundamental frequency and duration of speech signals, without affecting the segment identity – that is, without changing the formants. Normally, it’s an automatic algorithm, but here we do it the hard way – by hand! If you want to follow-along, you will need Audacity and these materials (a […]
Continue reading...Bitrate

The bitrate (or bit rate) of a signal is the number of bits required to store, or transmit, 1 s of that signal. A bit is a binary number: either 0 or 1. Let’s calculate the bitrate of a digital waveform. First you should revise the concepts of sampling and quantisation from this module of the […]
Continue reading...Classification and regression trees (CART)

A quick introduction to a very simple but widely-applicable model that can perform classification (predicting a discrete label) or regression (predicting a continuous value). The tree is learned from labelled data, using supervised learning. Before watching this video, you might want to check that you understand what Entropy is.
Continue reading...Token passing
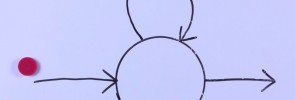
Token passing is a really nice way to understand (and even to implement) Viterbi search for Hidden Markov Models. Here we see token passing in action, and you can look at the spreadsheet to see the calculations. To keep things simple, we are ignoring transition probabilities in this example. It would be simple to add them […]
Continue reading...Interactive unit selection

Just a toy demo, but should give you some idea of how unit selection waveform generation works. Click with your mouse to choose a candidate diphone from each column, then the corresponding synthesised waveform will appear. You can click on the synthesised waveform to hear it again. Try to obtain the most natural-sounding synthesis by […]
Continue reading...Autocorrelation for estimating F0
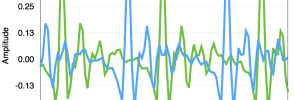
Most methods for estimating F0 start from autocorrelation. The idea is pretty simple: we are just looking for a repeating pattern in the waveform, which corresponds to the periodic vocal fold activity. For some waveforms, it might be possible to do that directly in the time domain, but in general that doesn’t work very well. […]
Continue reading...The Gaussian probability density function: understanding the equation
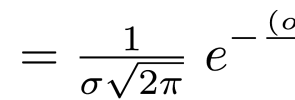
The equation for the Gaussian probability density function looks a little scary at first, but this video should help you understand what each of the terms is doing, and how they fit together. After watching the video download the spreadsheet which shows the calculations and plots from this video (tip: the Apple Numbers.app version includes images […]
Continue reading...Wave propagation on the surface of water

At the Alhambra (Granada, Spain) I saw this nice example of waves from a point source propagating in all directions at a fixed speed.
Continue reading...The speed of sound

At the Parque de las Ciencias in Granada, Spain there is this long tube, open at the end nearest you and closed at the far end. We can calculate the length of this tube just from the audio recording, because we know the speed of sound. Here’s the waveform of part of the recording, showing […]
Continue reading...Pipeline architecture for TTS
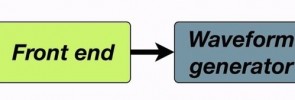
Most text-to-speech systems split the problem into two main stages. The first stage is called the front end and contains many separate processes which gradually build up a linguistic specification from the input text. The second stage typically uses language-independent techniques (although they still require a language-specific speech corpus) to generate a waveform. Here we see those two […]
Continue reading... This is the new version. Still under construction.
This is the new version. Still under construction.